AI Maturity: Creating a Self-Assessment
As AI continues to evolve, companies must take a structured approach to evaluating their current capabilities, identifying gaps, and strategically planning for the future. At Xima, I developed an AI self-assessment framework to benchmark where our existing product stood, where we needed to make progress, and what internal assets we could leverage to accelerate our AI initiatives.
This framework utilized a sliding scale of AI maturity models, allowing us to categorize our current and future AI capabilities with precision.
The AI Maturity Models
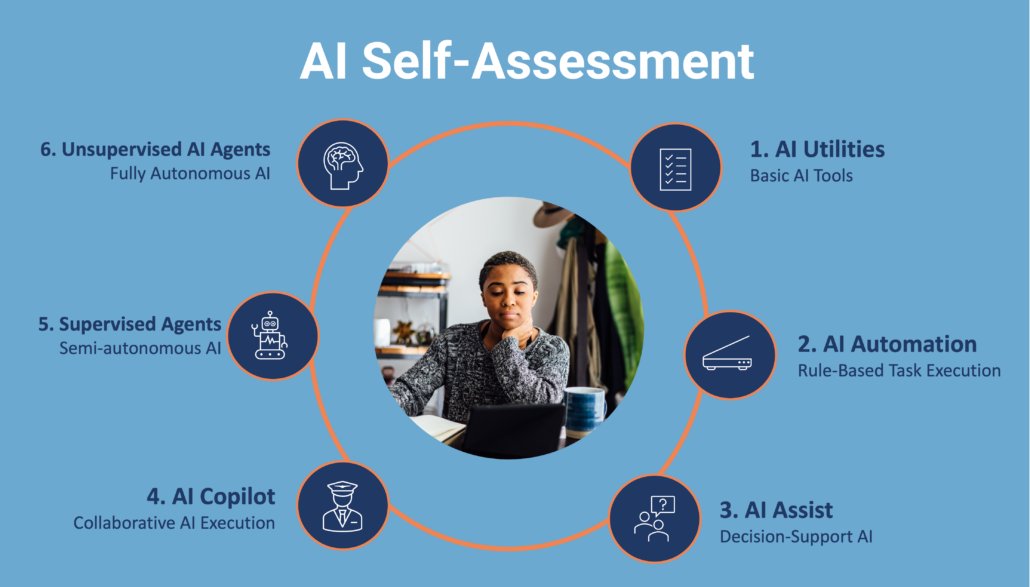
To guide our assessment, I structured AI maturity into six progressive categories:
1. AI Utilities (Basic AI Tools)
AI Utilities represent foundational AI functions that perform simple, predefined tasks without adaptability. These tools provide value by improving efficiency but lack autonomous decision-making capabilities.
-
Example: AI-driven spell-checkers, search autocomplete, and basic chatbots.
-
Assessment Insight: Understanding where AI Utilities played a role in our product helped us recognize where we had quick wins but limited strategic differentiation.
2. AI Automation (Rule-Based Task Execution)
AI Automation enhances efficiency by executing repetitive tasks without human intervention but follows strictly programmed logic.
-
Example: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for data processing, automated call routing, and AI-powered workflow management.
-
Assessment Insight: Identifying areas where AI Automation could replace manual processes allowed us to streamline internal operations and free up resources for higher-value AI initiatives.
3. AI Assist (Decision-Support AI)
AI Assist provides contextual recommendations and insights to users, improving decision-making without full autonomy.
-
Example: AI-driven analytics dashboards, intelligent email sorting, and virtual assistants that suggest but do not act independently.
-
Assessment Insight: Mapping our existing product features to this category helped us understand where AI was already enhancing user workflows and where it needed refinement.
4. AI Copilot (Collaborative AI for Execution)
An AI Copilot actively works alongside humans, providing real-time assistance, executing tasks, and adapting to context, but still requiring oversight.
-
Example: GitHub Copilot for code suggestions, AI-enhanced CRM tools, and AI-driven customer support assistants.
-
Assessment Insight: This stage represented a critical milestone in our roadmap. We identified specific product areas where an AI Copilot experience would provide tangible business value and improve user engagement.
5. Supervised AI Agents (Semi-Autonomous AI with Learning Capabilities)
Supervised AI Agents make independent decisions within a predefined scope, learning from human-labeled data and requiring periodic human validation.
-
Example: Fraud detection AI, AI-powered customer service chatbots with escalation capabilities, and self-driving cars in supervised mode.
-
Assessment Insight: We evaluated the data assets available to train supervised AI models and pinpointed opportunities to integrate them for more dynamic and proactive user experiences.
6. Unsupervised AI Agents (Fully Autonomous AI with Adaptive Learning)
The most advanced form of AI, Unsupervised AI Agents, can learn, adapt, and make decisions in real time without human intervention. These systems operate in highly complex environments and improve through self-learning mechanisms.
-
Example: Fully autonomous trading bots, self-learning cybersecurity AI, and generative AI models that continuously optimize user experiences.
-
Assessment Insight: This category helped us envision long-term AI goals, ensuring we had a roadmap that accounted for the data infrastructure, computational power, and governance models necessary to build toward AI autonomy.
How This Assessment Informed Our AI Roadmap
By mapping our product’s current capabilities against this AI maturity framework, we gained clear strategic insights that shaped our AI roadmap:
-
Identifying Quick Wins: Areas where we already had AI Utilities and Automation were leveraged to create immediate improvements in efficiency and user experience.
-
Prioritizing High-Impact AI Development: The transition from AI Assist to AI Copilot became a major focus, as it provided tangible value while still being technically feasible.
-
Building Toward AI Autonomy: While fully Unsupervised AI Agents were a long-term goal, we recognized that investing in Supervised AI Agents would provide stepping stones to gradually increase AI independence within our product.
-
Leveraging Internal AI Assets: The assessment allowed us to catalog existing data sources, machine learning models, and AI expertise within Xima to accelerate AI development without unnecessary duplication of effort.
Conclusion
An AI self-assessment is a critical strategic tool for any organization serious about AI-driven innovation. At Xima, using a structured AI maturity model helped us diagnose our current state, prioritize our AI initiatives, and establish a clear roadmap for future progress.
As AI capabilities evolve, this self-assessment will serve as a living framework—guiding our decision-making, ensuring alignment with business objectives, and maintaining a competitive edge in the AI landscape.



